Difference between revisions of "KHIKA App for Fortigate Firewall"
(→Some suggestions for useful interaction with this dashboard could be :) |
(→Fortigate Firewall Alerts) |
||
| Line 299: | Line 299: | ||
| − | Alerts are generated when certain | + | Alerts are generated when certain critical behavior is observed in the system. Alerts can be monitored in real-time on Alerts Dashboard in KHIKA. Relevant stakeholders can also receive the alerts via emails. The table below explains all the pre-canned alerts shipped with KHIKA App for Fortigate firewall. |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
==== Alerts Description ==== | ==== Alerts Description ==== | ||
| Line 314: | Line 311: | ||
|- | |- | ||
|Fortigate firewall successful sweep scan activity by malicious ip | |Fortigate firewall successful sweep scan activity by malicious ip | ||
| − | |This alert is triggered when more than 10 | + | |This alert is triggered when more than 10 connection attempts happen from same 'malicious IP' and status is 'deny', followed by a successful connection where status is 'accept'. This all has to happen on unique Destination IPs, within one minute |
| − | |Bad ip address tries to spray connection requests on one of the popular ports (21,22,53,80,443 etc) on multiple IP addresses with an intention to find which ports are opened on what IP addresses. Typically, scan attempt is the first stage of reconnaissance in the attack life cycle | + | |Bad ip address tries to spray connection requests on one of the popular ports (21,22,53,80,443 etc) on multiple IP addresses with an intention to find which ports are opened on what IP addresses. Typically, scan attempt is the first stage of reconnaissance in the attack life cycle. An attacker finds an open port on one of ip addresses and is able to establish a connection. The attacker can then start the next stage in the attack. Spotting these attacks early is important. |
It is important to check the reputation of the external ip address and block the same if necessary. | It is important to check the reputation of the external ip address and block the same if necessary. | ||
| − | It is also important to verify the sanity of affected internal nodes by checking if any unwarranted system policy change or software configuration/updates have | + | It is also important to verify the sanity of affected internal nodes by checking if any unwarranted system policy change or software configuration/updates have occurred during the affected time period. If required, quarantine the affected servers till the time the issues are resolved. |
|- | |- | ||
|Fortigate firewall host scan activity by malicious ip | |Fortigate firewall host scan activity by malicious ip | ||
| − | |This alert is triggered when more than 10 | + | |This alert is triggered when more than 10 connection attempts happen from the same malicious IP using different destination port targeting a single destination host, within one minute |
| − | |Bad ip address tries to spray connection requests on multiple popular ports (21,22,53,80,443 etc) | + | |Bad ip address tries to spray connection requests on multiple popular ports (21,22,53,80,443 etc) targeting one single IP address at a time with an intention to find the open ports on the target IP address. Typically, scan attempt is the first stage of reconnaissance in the attack life cycle. |
It is important to check the reputation of the external ip address and block the same if necessary. | It is important to check the reputation of the external ip address and block the same if necessary. | ||
|- | |- | ||
|Fortigate firewall large data sent outside | |Fortigate firewall large data sent outside | ||
| − | |This alert is triggered when large data is sent to | + | |This alert is triggered when large data is sent to an external IP Address. |
| − | |Large amount of data being sent to an external network could be an indication of data | + | |Large amount of data being sent to an external network could be an indication of data ex-filtration.<br/><br/> |
| − | Check with the user or process which is responsible for the data being sent out and whether it was done for legitimate business reasons. This could be a false positive. | + | Check with the user or process which is responsible for the data being sent out and whether it was done for legitimate business reasons. This could be a false positive but worth investigating. |
|- | |- | ||
|Fortigate firewall critical message reported by firewall management software | |Fortigate firewall critical message reported by firewall management software | ||
|This alert is triggered when a critical level message is logged. | |This alert is triggered when a critical level message is logged. | ||
|This message is generated by the firewall itself. It may indicate some operational issue that must be addressed.<br/><br/> | |This message is generated by the firewall itself. It may indicate some operational issue that must be addressed.<br/><br/> | ||
| − | The admin may refer to firewall manual to take required action (the issue could be related to | + | The admin may refer to firewall manual to take the required action (the issue could be related to resource utilization, errors or equivalent). |
|- | |- | ||
|Fortigate firewall sweep scan attack by malicious ip | |Fortigate firewall sweep scan attack by malicious ip | ||
| − | |This alert is triggered when more than 10 | + | |This alert is triggered when more than 10 connection attempts happen from the same malicious IP targeting different Destination IP's, within one minute |
|Bad ip addresses tries to spray connection requests on one of the popular ports (21,22,53,80,443 etc) on multiple IP addresses with an intention to find which ports are opened on what IP addresses. Typically, scan attempt is the first stage of reconnaissance in the attack life cycle.<br/><br/> | |Bad ip addresses tries to spray connection requests on one of the popular ports (21,22,53,80,443 etc) on multiple IP addresses with an intention to find which ports are opened on what IP addresses. Typically, scan attempt is the first stage of reconnaissance in the attack life cycle.<br/><br/> | ||
It is important to check the reputation of the external ip address and block the same if necessary. | It is important to check the reputation of the external ip address and block the same if necessary. | ||
|- | |- | ||
|Fortigate firewall sweep scan attack | |Fortigate firewall sweep scan attack | ||
| − | |This alert is triggered when more than 10 connections happened from the same source IP to various Destination IP's, within one minute. | + | |This alert is triggered when more than 10 connections happened from the same source IP to various Destination IP's, within one minute. This IP address need not be malicious as per KHIKA threat intelligence. |
|An attacker tries to spray connection requests on one of the popular ports (21,22,53,80,443 etc) on multiple IP addresses with an intention to find which ports are opened on what IP addresses. Typically, scan attempt is the first stage of reconnaissance in the attack life cycle.<br/><br/> | |An attacker tries to spray connection requests on one of the popular ports (21,22,53,80,443 etc) on multiple IP addresses with an intention to find which ports are opened on what IP addresses. Typically, scan attempt is the first stage of reconnaissance in the attack life cycle.<br/><br/> | ||
| − | Unless it is a known and legitimate IP address performing scan, it is important to block this IP. You may | + | Unless it is a known and legitimate IP address performing scan, it is important to block this IP. You may white-list the known IP addresses (such as designated Vulnerability Scanner, Asset Discovery Tools etc), so as to suppress the false positives. |
|- | |- | ||
|Fortigate firewall host scan attack | |Fortigate firewall host scan attack | ||
|This alert is triggered when more than 10 connections happened from the same Source IP and Destination IP using different destination port, within one minute | |This alert is triggered when more than 10 connections happened from the same Source IP and Destination IP using different destination port, within one minute | ||
| − | |An attacker tries to spray connection requests on multiple popular ports (21,22,53,80,443 etc) | + | |An attacker tries to spray connection requests on multiple popular ports (21,22,53,80,443 etc) targeting one single IP addresses at a time with an intention to find the open ports on the target IP address. Typically, scan attempt is the first stage of reconnaissance in the attack life cycle.<br/><br/> |
| − | Unless it is a known and legitimate IP address performing the scan, it is important to block this IP. You may | + | Unless it is a known and legitimate IP address performing the scan, it is important to block this IP. You may white-list the known IP addresses (such as designated Vulnerability Scanner, Asset Discovery Tools etc), so as to suppress the false positives. |
|- | |- | ||
|Fortigate firewall successful host scan activity by malicious ip | |Fortigate firewall successful host scan activity by malicious ip | ||
| Line 365: | Line 362: | ||
|- | |- | ||
|Fortigate firewall backdoor traffic detected | |Fortigate firewall backdoor traffic detected | ||
| − | |This alert is triggered when connection | + | |This alert is triggered when connection happens on uncommon and vulnerable Destination ports like 3127,3198,6129,7080 |
| − | |This event indicates that a traffic is generated | + | |This event indicates that a traffic is generated to internal machine on vulnerable ports(3127,3198,6129,7080). Typically, these ports are used by attacker to exploit vulnerable programs listening on these ports.<br/><br/> |
| − | Check | + | Check if these ports are opened and on what servers. Ask question, do you really need these ports opened?<br/><br/> |
Check what programs are running on these ports. Check vulnerability reports of the applications.<br/><br/> | Check what programs are running on these ports. Check vulnerability reports of the applications.<br/><br/> | ||
Block these ports for external traffic, unless mandatory to keep them opened.<br/><br/> | Block these ports for external traffic, unless mandatory to keep them opened.<br/><br/> | ||
| Line 374: | Line 371: | ||
|- | |- | ||
|Fortigate firewall communication with possible IOC or bad IP | |Fortigate firewall communication with possible IOC or bad IP | ||
| − | |This alert is triggered when suspicious IP is | + | |This alert is triggered when a suspicious IP is communicating with internal IP |
|KHIKA shares community based threat intelligence (TI) every 24 hours. TI has list of IP addresses with bad reputation. Every bad IP is marked with number of communities reporting it, name of each community and confidence indicating how confident are we about the reputation. This alert is generated when communication with a bad IP is let through.<br/><br/> | |KHIKA shares community based threat intelligence (TI) every 24 hours. TI has list of IP addresses with bad reputation. Every bad IP is marked with number of communities reporting it, name of each community and confidence indicating how confident are we about the reputation. This alert is generated when communication with a bad IP is let through.<br/><br/> | ||
| − | If communication with a bad IP is happening, it must be blocked immediately as it could be a possible attack or data exfiltration.<br/><br/> | + | If communication with a bad IP is happening, it must be blocked immediately as it could be a possible attack or a data exfiltration.<br/><br/> |
| − | You can check how | + | You can check how long this communication is happening by simply searching the malicious IP in the logs. You can also check what internal IP addresses are communicating with the malicious IP address and track the real users behind those internal IP addresses.<br/><br/> |
Cross-check the reputation of the IP with popular websites such as ipvoid.com, virustotal.com.<br/><br/> | Cross-check the reputation of the IP with popular websites such as ipvoid.com, virustotal.com.<br/><br/> | ||
| − | If you see an internal IP constantly getting involved in malicious communication (with same or multiple external IP addresses), you may install agents on the internal nodes involved and check the real user and process responsible for this communication.<br/><br/> | + | If you see an internal IP constantly getting involved in malicious communication (with same or multiple external IP addresses), you may install agents on the internal nodes involved and check the real user and process responsible for this communication. An EDR solution would be helpful in such cases.<br/><br/> |
It is critical to block this rogue communication. | It is critical to block this rogue communication. | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | |Fortigate firewall | + | |Fortigate firewall exchanging data with suspicious IP |
|This alert is triggered when bytes are send and receive during communication with maliacious IP. | |This alert is triggered when bytes are send and receive during communication with maliacious IP. | ||
| − | | | + | |If communication with a bad IP is happening, it must be blocked immediately as it could be a possible attack or a data exfiltration. |
You can check the log for this communication by simply searching the malicious IP in the logs. You can also check which internal IP addresses are communicating with this IP address and track the real users behind those internal IP addresses.<br/><br/> | You can check the log for this communication by simply searching the malicious IP in the logs. You can also check which internal IP addresses are communicating with this IP address and track the real users behind those internal IP addresses.<br/><br/> | ||
| − | If you see an internal IP constantly getting involved in malicious communication (with same or multiple external IP addresses), you may install agents on the internal nodes involved and check the real user and process responsible for this communication.<br/><br/> | + | If you see an internal IP constantly getting involved in malicious communication (with same or multiple external IP addresses), you may install agents on the internal nodes involved and check the real user and process responsible for this communication. An EDR solution may help in such cases<br/><br/> |
If required, quarantine the affected internal servers till the time the issues are resolved. | If required, quarantine the affected internal servers till the time the issues are resolved. | ||
|- | |- | ||
Revision as of 10:22, 25 June 2019
Contents
- 1 Introduction
- 2 Enabling Syslog forwarding on the device
- 3 Verifying SYSLOG data collection
- 4 How to Install the KHIKA App for Fortigate Firewall?
- 5 Adding the device in the Adaptor
- 6 How to check the output of KHIKA Fortigate App ?
Introduction
Most of the network devices, such as firewalls, switches, routers, web proxies etc send the traffic and user activity related information in the form of logs over syslog protocol. Foritgate firewall also supports syslog protocol that makes integration with SIEM possible. KHIKA Data Aggregator is pre-configured with syslog services on port 514. The key parts to get here are :
- Enabling Syslog forwarding on the Fortigate device
- Install the KHIKA App for Fortigate Firewall
- Get data from your Fortigate Firewall into KHIKA Aggregator
Enabling Syslog forwarding on the device
Please refer to Fortigate Documentation for enabling syslogs on your firewall device.
Example of commands to be fired on Firewall Device to enable syslogs:
config log syslogd setting set csv disable set facility syslog3 set port 514 set reliable disable set server IP_OF_KHIKA_DATA_AGGREGATOR set status enable end
Note that we do not use CSV format. We recommend you referring to the exact documentation of the OEM that matches the version of the product you are using.
To forward FortiAnalyzer events do following steps
Log in to your FortiAnalyzer device. On the Advanced tree menu, select Syslog Server. On the toolbar, click Create New. Configure the Syslog Server parameters: set Port to 514 (UDP) set server to IP Address of KHIKA Data Aggregator Click OK.
Verifying SYSLOG data collection
After you enable the syslog forwarding on the end device, you must verify if the logs are being really received by KHIKA Data Aggregator. Please refer here to understand how to verify syslogs on KHIKA Data Aggregator.
How to Install the KHIKA App for Fortigate Firewall?
It is assumed, that you have already configured KHIKA Data Aggregator in your environment. If not, please read how to configure KHIKA Data Aggregator and perform the pre-requisite steps.
This section explains how to pick and install the KHIKA application for Fortigate Firewall . Installing the application shall put together and activate the adapter (parser) that can handle Fortigate Firewall data format, the dashboards and the alert rules preconfigured.
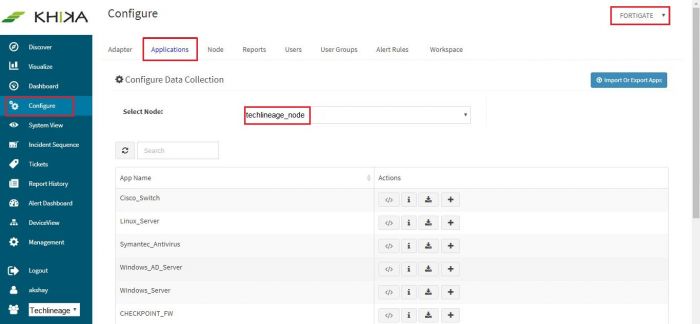
Go to “Applications” tab in the “Configure” menu.
Check whether the appropriate Workspace is selected. Note: Application is always loaded in a Workspace. Read the section on Workspaces to know more about KHIKA Workspaces. Also select your KHIKA aggregator name in the Node dropdown. This is to ensure that we are collecting data from the desired source and into the correct workspace which is ready with the configured application and components.
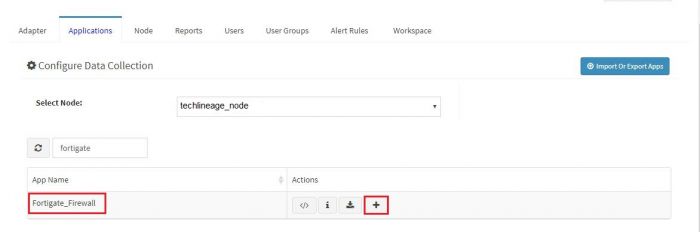
Click on the “+” button. A pop up appears.
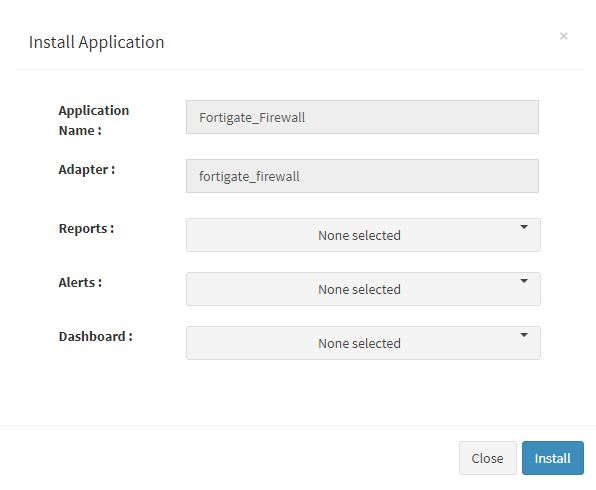
User can now select the contents of the application required. For example, on the dropdown for “Reports”, click to expand it. List of all reports can be seen. User can individually select the reports required by checking on the checkbox next to each. Alternatively, check on “Select All” option to get all of them. Similarly you can select contents from Alerts and Dashboards.
Visit the sections on KHIKA Reports, KHIKA Dashboards, KHIKA Alerts & Correlations to know more about these topics.
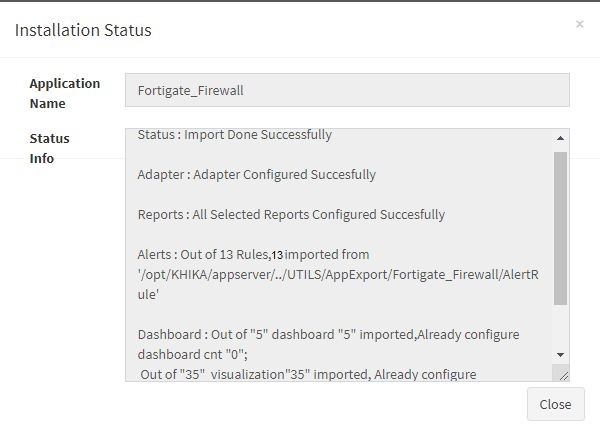
Click “OK” to proceed with the installation of the selected Application. After successful installation, following status should be displayed :
This simple procedure to install a KHIKA App, automatically configures the Adapter (required for parsing the data from raw syslogs), calculated KHIKA reports on raw data, Visualizations, Dashboards and Alerts – all in one click.
Adding the device in the Adaptor
After syslogs are enabled on the device and the App is installed into KHIKA, it is the time to add the device to the this App (in Adapter section of KHIKA Web GUI). Please refer here to know how to add the device to an App.
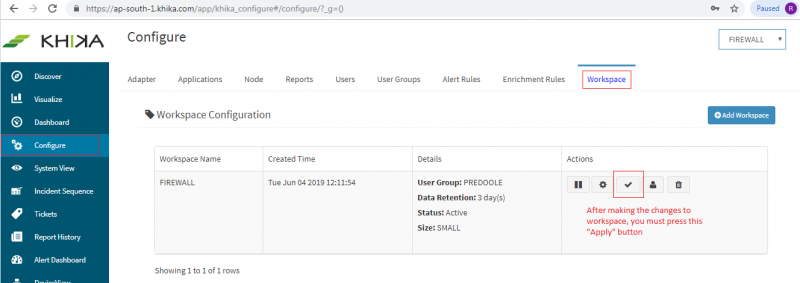
After making these configuration in KHIKA, you must apply these changes to the Workspace. Go to Configure, select the Workspace and in Workspace tab of configure menu press the Apply button as shown in the screenshot below.
Wait for a few minutes for changes to apply and data to arrive in kHIKA. With all these steps, we should now expect the data to arrive in KHIKA. Lets discover some live data in KHIKA.
How to check the output of KHIKA Fortigate App ?
Discovering the logs of Fortigate Firewall
After doing all the steps given above, we should start receiving live data into KHIKA. Go to "Discover" section in KHIKA GUI and select the index with name "*raw-fortigate_firewall*". Note that the index has a prefix of the customer name and workspace name. After selecting this index, you should see the live data coming in. Spend some time understanding this data and the fields of the data.
Fortigate Firewall Attack Dashboard
Go to "Dashboards" from the left menu. From the list of in-built dashboards, select this one (you can also search for it). This dashboard focuses on the attack information like attack name, action taken by the fortigate firewall, sourceIP and destinationIP etc. You can filter and search information and create new ones too. For help on Dashboards, click here
Elements in the Dashboard are explained below :
| Visualization | Description |
| Attack wise Action bar graph | X axis : Differnt types of attack on fortigate firewall Y axis : Action performed on attack and it's count. |
| Contribution of Severity and Action multi-level pie chart | Different types of Severities like critical, info, error, warning and Action(s) performed like clear_session on fortiagte firewall. |
| SourceIP wise Attack bar graph | X axis : source IP(s). Y axis : Different types of attacks and it's count. |
| DestinationIP wise Attack bar graph | X axis : Destination IP(s). Y axis : Different types of attacks and it's count. |
| Daily Trend | Trend of events over time. Useful to identify unusual spikes at a glance. X axis : date & time Y axis : count of events |
| Contribution of Service pie chart | Contribution of different types of services like https, http, ping on fortigate firewall. |
| Summary Table | Detailed data with timestamp and count |
Suggestion for useful interaction with this dashboard could be :
- Click on “Attack” in the "Attack wise Action" bar graph. This gets selected and shows the different types of attacks and actions taken for the selected attack. The next bar shall show sourceIP and destinationIP. The next pie shall shows different types of "severities" and "services" on the fortigate firewall. Details of the selected attack can be seen in the summary table. How to remove this filter is explained here
Fortigate Firewall MaliciousIP Dashboard
Go to "Dashboards" from the left menu. From the list of in-built dashboards, select this one. It shall open the Dashboard. This dashboard focuses on the fortigate firewall communication with suspicious IP(s). Details like bad IPs, Source IP/Destination IPs, communication with internal IP are seen.
You can filter and search information and create new ones too. For help with Dashboards, click here
Elements in the Dashboard are explained below :
| Visualization | Description |
| Contribution of Action pie chart | Contribution of the status of connection.Example allow, deny etc. |
| Malicious IP wise Action bar chart | X axis : All the MaliciousIP(s) that are communicating Y axis : MaliciousIP wise Action and the count. |
| SourceIP wise Hits bar graph | X axis : All the Source IP(s) that initiate the connection Y axis : SourceIP wise number of hits. |
| DestinationIP wise Hits bar graph | X axis : All the Destination IP(s) that communicate to malicious IPs Y axis : DestinationIP wise number of hits. |
| Contribution of service pie chart | Contribution of different types of services like snmp of fortigate firewall. |
| Contribution of level pie chart | Contribution of different types of levels like notice of fortigate firewall. |
| Daily Trend | Trend of events over time. Useful to identify unusual spikes at a glance. X axis : date & time Y axis : count of events |
| Summary Table | Detailed data with timestamp and count |
A suggestion for useful interaction with this dashboard could be :
- Click on “MaliciousIP” in the "Malicious IP wise Action" bar graph. This gets selected and shows the actions for selected Malicious IP. The next bar shall show Source IP and Destination IP for selected malicious communication. The next pie shall show different types of "action", "services" and "levels" for selected Malicious IP. Details about selected Malicious IP can be seen in the summary table. How to remove this filter is explained here
Fortigate Firewall System Activities Dashboard
Go to "Dashboards" from the left menu. From the list of in-built dashboards, select this one. It shall open the Dashboard. This dashboard summarizes self monitoring system event and also command,action executed by user etc.
You can filter and search information and create new ones too. For help with Dashboards, click here
Elements in the Dashboard are explained below :
| Visualization | Description |
| Contribution of Action pie chart | Contribution of action performed by a particular user on the fortigate firewall. |
| User wise Action bar graph | X axis : user(s) Y Axis : Action performed by a particular user and it's count. |
| Contribution of Status pie chart | Contribution of different types of status. |
| Contribution of level pie chart | Contribution of different types of levels like notice, warning, etc. for event |
| LogDesc wise Message bar graph | X axis : Logdesc Y axis : Logdesc wise message and it's count. |
| Daily Trend | Trend of events over time. Useful to identify unusual spikes at a glance. X axis : date & time Y axis : count of events |
| Summary Table | Detailed data with timestamp and count |
Some suggestions for useful interaction with this dashboard could be :
- Click on “User” in the "User wise Action" bar graph. This gets selected and shows the actions performed by selected User on fortigate firewall. The next bar shall shows messages for selected User on fortigate firewall. The next pie shall shows different types of "status", "action" and "levels". Details of all activities performed by selected user can be seen in the summary table. How to remove this filter is explained here
Fortigate Firewall VPN Dashboard
Go to "Dashboards" from the left menu. From the list of in-built dashboards, select this one. It shall open the Dashboard.This dashboard focuses on the VPN login activities on fortigate firewall. Details like type of VPN, Source IP,Destination IP etc.
You can filter and search information and create new ones too. For help with Dashboards, click here
Elements in the Dashboard are explained below :
| Visualization | Description |
| Contribution of VPN pie chart | Contribution of different types of VPN on fortigate firewall. |
| Contribution of VPN Type pie chart | Contribution of different types VPN type on fortigate firewall. |
| SourceIP wise Hits | X axis : SourceIP(s) Y axis : SourceIP wise number of hits. |
| DestinationIP wise Hits | X axis : DestinationIP(s) Y axis : DestinationIP wise number of hits. |
| Contribution of Service pie chart | Contribution of different types of services like snmp,syslog of fortigate firewall. |
| Daily Trend | Trend of events over time. Useful to identify unusual spikes at a glance. X axis : date & time Y axis : count of events |
| Summary Table | Detailed data with timestamp and count |
Some suggestions for useful interaction with this dashboard could be :
- Click on particular VPN tunnel in the "Contribution of VPN" pie chart. This gets selected and shows the VPN name.The next bar shall show sourceIP which intiate VPN connection and destinationIP(server IP) which is accessed by Source IP. The next pie shall shows differnt types of "VPN types" and "services" of fortigate firewall.Details of selected VPN information can be seen in the summary table.How to remove this filter is explained here
Fortigate Firewall VPNTunnel Dashboard
Go to "Dashboards" from the left menu. From the list of in-built dashboards, select this one. It shall open the Dashboard. This dashboard focuses on the VPN Tunnel information like VPN Tunnel , Status etc.You can filter and search information and create new ones too. For help with Dashboards, click here
Elements in the Dashboard are explained below :
| Visualization | Description |
| Contribution of VPN Tunnel pie chart | Contribution of differnt VPN Tunnel on fortigate firewall. |
| Contribution of Status pie chart | Contribution of status like sucess/failure. |
| Remote IP wise Hits bar graph | X axis : Remote IP(s) Y axis : Remote IP wise number of hits. |
| Local IP wise Hits bar graph | X axis : Local IP(s) Y axis : Local IP wise number of hits. |
| Daily Trend | Trend of events over time. Useful to identify unusual spikes at a glance. X axis : date & time Y axis : count of events |
| Summary Table | Detailed data with timestamp and count |
Some suggestions for useful interaction with this dashboard could be :
- Click on “VPN Type” in the "Contribution of VPN Tunnel" bar graph. This gets selected and shows the VPN Tunnel information . The next bar shall shows RemoteIP which is a SourceIP and LocalIP accessed. The next pie shall shows different types of status like success/failure. Details about selected VPN traffic can be seen in the summary table. How to remove this filter is explained here
Fortigate Firewall Alerts
Alerts are generated when certain critical behavior is observed in the system. Alerts can be monitored in real-time on Alerts Dashboard in KHIKA. Relevant stakeholders can also receive the alerts via emails. The table below explains all the pre-canned alerts shipped with KHIKA App for Fortigate firewall.
Alerts Description
| Alert Name | Description | Suggested Resolution |
| Fortigate firewall successful sweep scan activity by malicious ip | This alert is triggered when more than 10 connection attempts happen from same 'malicious IP' and status is 'deny', followed by a successful connection where status is 'accept'. This all has to happen on unique Destination IPs, within one minute | Bad ip address tries to spray connection requests on one of the popular ports (21,22,53,80,443 etc) on multiple IP addresses with an intention to find which ports are opened on what IP addresses. Typically, scan attempt is the first stage of reconnaissance in the attack life cycle. An attacker finds an open port on one of ip addresses and is able to establish a connection. The attacker can then start the next stage in the attack. Spotting these attacks early is important.
It is important to check the reputation of the external ip address and block the same if necessary. It is also important to verify the sanity of affected internal nodes by checking if any unwarranted system policy change or software configuration/updates have occurred during the affected time period. If required, quarantine the affected servers till the time the issues are resolved. |
| Fortigate firewall host scan activity by malicious ip | This alert is triggered when more than 10 connection attempts happen from the same malicious IP using different destination port targeting a single destination host, within one minute | Bad ip address tries to spray connection requests on multiple popular ports (21,22,53,80,443 etc) targeting one single IP address at a time with an intention to find the open ports on the target IP address. Typically, scan attempt is the first stage of reconnaissance in the attack life cycle.
It is important to check the reputation of the external ip address and block the same if necessary. |
| Fortigate firewall large data sent outside | This alert is triggered when large data is sent to an external IP Address. | Large amount of data being sent to an external network could be an indication of data ex-filtration. Check with the user or process which is responsible for the data being sent out and whether it was done for legitimate business reasons. This could be a false positive but worth investigating. |
| Fortigate firewall critical message reported by firewall management software | This alert is triggered when a critical level message is logged. | This message is generated by the firewall itself. It may indicate some operational issue that must be addressed. The admin may refer to firewall manual to take the required action (the issue could be related to resource utilization, errors or equivalent). |
| Fortigate firewall sweep scan attack by malicious ip | This alert is triggered when more than 10 connection attempts happen from the same malicious IP targeting different Destination IP's, within one minute | Bad ip addresses tries to spray connection requests on one of the popular ports (21,22,53,80,443 etc) on multiple IP addresses with an intention to find which ports are opened on what IP addresses. Typically, scan attempt is the first stage of reconnaissance in the attack life cycle. It is important to check the reputation of the external ip address and block the same if necessary. |
| Fortigate firewall sweep scan attack | This alert is triggered when more than 10 connections happened from the same source IP to various Destination IP's, within one minute. This IP address need not be malicious as per KHIKA threat intelligence. | An attacker tries to spray connection requests on one of the popular ports (21,22,53,80,443 etc) on multiple IP addresses with an intention to find which ports are opened on what IP addresses. Typically, scan attempt is the first stage of reconnaissance in the attack life cycle. Unless it is a known and legitimate IP address performing scan, it is important to block this IP. You may white-list the known IP addresses (such as designated Vulnerability Scanner, Asset Discovery Tools etc), so as to suppress the false positives. |
| Fortigate firewall host scan attack | This alert is triggered when more than 10 connections happened from the same Source IP and Destination IP using different destination port, within one minute | An attacker tries to spray connection requests on multiple popular ports (21,22,53,80,443 etc) targeting one single IP addresses at a time with an intention to find the open ports on the target IP address. Typically, scan attempt is the first stage of reconnaissance in the attack life cycle. Unless it is a known and legitimate IP address performing the scan, it is important to block this IP. You may white-list the known IP addresses (such as designated Vulnerability Scanner, Asset Discovery Tools etc), so as to suppress the false positives. |
| Fortigate firewall successful host scan activity by malicious ip | This alert is triggered when more than 10 connections happened from the same malicious IP and status is deny followed by a successful login status using different destination port, within one minute. | Bad ip address tries to spray connection requests on multiple popular ports (21,22,53,80,443 etc) targetting one single IP addresses at a time with an intention to find the open ports on the target IP address. Typically, scan attempt is the first stage of reconnaissance in the attack life cycle and attacker done successful connection on open ports. It is important to check the reputation of the external ip address and block the same if necessary. |
| Fortigate firewall successful host scan activity | This alert is triggered when more than 10 connections happened from the same Source and Destination IP and status is deny followed by a successful login status using different destination port, within one minute. | Attacker tries to spray connection requests on multiple popular ports (21,22,53,80,443 etc) targetting one single IP addresses at a time with an intention to find the open ports on the target IP address. Typically, scan attempt is the first stage of reconnaissance in the attack life cycle and attacker done successful connection on open ports. It is important to check the reputation of the suspected ip address. |
| Fortigate firewall backdoor traffic detected | This alert is triggered when connection happens on uncommon and vulnerable Destination ports like 3127,3198,6129,7080 | This event indicates that a traffic is generated to internal machine on vulnerable ports(3127,3198,6129,7080). Typically, these ports are used by attacker to exploit vulnerable programs listening on these ports. Check if these ports are opened and on what servers. Ask question, do you really need these ports opened? |
| Fortigate firewall communication with possible IOC or bad IP | This alert is triggered when a suspicious IP is communicating with internal IP | KHIKA shares community based threat intelligence (TI) every 24 hours. TI has list of IP addresses with bad reputation. Every bad IP is marked with number of communities reporting it, name of each community and confidence indicating how confident are we about the reputation. This alert is generated when communication with a bad IP is let through. If communication with a bad IP is happening, it must be blocked immediately as it could be a possible attack or a data exfiltration. |
| Fortigate firewall exchanging data with suspicious IP | This alert is triggered when bytes are send and receive during communication with maliacious IP. | If communication with a bad IP is happening, it must be blocked immediately as it could be a possible attack or a data exfiltration.
You can check the log for this communication by simply searching the malicious IP in the logs. You can also check which internal IP addresses are communicating with this IP address and track the real users behind those internal IP addresses. |
| Fortigate firewall successful sweep scan activity | This alert is triggered when more than 10 connections happened from the same Source IP and status is deny followed by a successful login status using different Destination IP, within one minute. | Attacker tries to spray connection requests on one of the popular ports (21,22,53,80,443 etc) on multiple IP addresses with an intention to find which ports are opened on what IP addresses. Typically, scan attempt is the first stage of reconnaissance in the attack life cycle and attacker done successful connection on one of ip addresses. It is important to check the reputation of the suspected ip address. |