Difference between revisions of "KHIKA App for PaloAlto Firewall"
(→Enabling Syslog forwarding on the device) |
(→A suggestion for useful interaction with this dashboard could be :) |
||
| (79 intermediate revisions by 3 users not shown) | |||
| Line 4: | Line 4: | ||
The key parts to get here are : | The key parts to get here are : | ||
#Enabling Syslog forwarding on the device | #Enabling Syslog forwarding on the device | ||
| − | #Install the KHIKA App for | + | #Install the KHIKA App for PaloAlto Firewall |
| − | #Get data from your | + | #Get data from your PaloAlto Firewall into KHIKA Aggregator |
== Enabling Syslog forwarding on the device == | == Enabling Syslog forwarding on the device == | ||
| − | For | + | you are recommended to refer to [https://docs.paloaltonetworks.com/pan-os/7-1/pan-os-admin/monitoring/configure-syslog-monitoring# Paloalto documentation] for enabling syslogs on your firewall device. |
| + | |||
| + | You can refer below suggested steps for enabling syslogs on your PaloAlto firewall device. | ||
| + | |||
| + | 1.Configure a Syslog server profile | ||
| + | 1.Select Device > Server Profiles > Syslog. | ||
| + | 2.Click Add and enter a Name for the profile. | ||
| + | 3.If the firewall has more than one virtual system (vsys), select the Location (vsys or Shared) where this profile is available. | ||
| + | 4.For each syslog server, click Add and enter the information that the firewall requires to connect to it: | ||
| + | Name — Unique name for the server profile. | ||
| + | Syslog Server — IP address or fully qualified domain name (FQDN) of the syslog server. | ||
| + | Transport — Select TCP, UDP, or SSL as the method of communication with the syslog server. | ||
| + | Port —The port number on which to send syslog messages (default is UDP on port 514); you must use the same port number on the firewall and the syslog | ||
| + | server. | ||
| + | Format —Select the syslog message format to use: BSD (the default) or IETF. Traditionally, BSD format is over UDP and IETF format is over TCP or SSL. | ||
| + | Facility —Select a syslog standard value (default is LOG_USER) to calculate the priority (PRI) field in your syslog server implementation. Select the | ||
| + | value that maps to how you use the PRI field to manage your syslog messages. | ||
| + | 5.Click OK to save the server profile. | ||
| + | |||
| + | 2.Configure syslog forwarding for Traffic, Threat, and WildFire Submission logs.</br> | ||
| + | 1.Create a log forwarding profile. | ||
| + | For creating log forwarding profile please refer this [https://docs.paloaltonetworks.com/pan-os/7-1/pan-os-admin/monitoring/configure-log-forwarding.html#20823# log forwarding profile] | ||
| + | Select Objects > Log Forwarding, click Add, and enter a Name to identify the profile. | ||
| + | For each log type and each severity level or WildFire verdict, select the Syslog server profile and click OK. | ||
| + | 2.Assign the log forwarding profile to security rules. | ||
| + | For creating log forwarding profile to security rules please refer this [https://docs.paloaltonetworks.com/pan-os/7-1/pan-os-admin/monitoring/configure-log-forwarding.html#33435 log forwarding profile to security rules] | ||
| + | |||
| + | 3. Configure syslog forwarding for System, Config, HIP Match, and Correlation logs. | ||
| + | Select Device > Log Settings. | ||
| + | For System and Correlation logs, click each Severity level, select the Syslog server profile, and click OK. | ||
| + | ` For Config, HIP Match, and Correlation logs, edit the section, select the Syslog server profile, and click OK. | ||
| + | |||
| + | 4. Commit your changes and review the logs on the syslog server. | ||
| + | Click Commit. | ||
| + | To review the logs, refer to the documentation of your syslog management software. | ||
| + | |||
| + | == Verifying SYSLOG data collection == | ||
| + | |||
| + | For help to verifying syslog data collection click [[Getting Data into KHIKA#Verifying syslog data collection|here]]. | ||
| + | |||
| + | == How to Install the KHIKA App for PaloAlto Firewall? == | ||
| + | |||
| + | It is assumed, that you have already configured KHIKA Data Aggregator in your environment. If not, please read [[Getting Started with KHIKA SaaS#Installing and configuring KHIKA Data Aggregator|how to configure KHIKA Data Aggregator]] and perform the pre-requisite steps. | ||
| + | |||
| + | This section explains how to pick and install the KHIKA application for PaloAlto Firewall . Installing the application shall put together and activate the adapter (parser) that can handle PaloAlto Firewall data format, the dashboards and the alert rules preconfigured. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Go to “Applications” tab in the “Configure” menu. | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[File:paloalto_application_tab11.jpg|700px]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | Check whether the appropriate Workspace is selected. | ||
| + | Note: Application is always loaded in a Workspace. Read the section on Workspaces to know more about KHIKA Workspaces. | ||
| + | Also select your KHIKA aggregator name in the Node dropdown. | ||
| + | This is to ensure that we are collecting data from the desired source and into the correct workspace which is ready with the configured application and components. | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[File:paloalto_application.jpg|700px]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | Click on the “+” button. A pop up appears. | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[File:paloalto_application_install.jpg|700px]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | User can now select the contents of the application required. For example, on the dropdown for “Reports”, click to expand it. List of all reports can be seen. User can individually select the reports required by checking on the checkbox next to each. Alternatively, check on “Select All” option to get all of them. | ||
| + | Similarly you can select contents from Alerts and Dashboards. | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[KHIKA Reports|What are KHIKA Reports]]<br> | ||
| + | [[KHIKA Dashboards|What are KHIKA Dashboards]]<br> | ||
| + | [[KHIKA Alerts|What are KHIKA Alerts]]<br> | ||
| + | |||
| + | Click “OK” to proceed with the installation of the selected Application. | ||
| + | After successful installation, following status should be displayed : | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[File:paloalto_application_status.jpg|700px]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | This simple procedure to install a KHIKA App, automatically configures the Adapter (required for parsing the data from raw syslogs), calculated KHIKA reports on raw data, Visualizations, Dashboards and Alerts – all in one click. | ||
| + | |||
| + | == Adding the device in the Adaptor == | ||
| + | After syslogs are enabled on the device and the App is installed into KHIKA, it is the time to add the device to the this App (in Adapter section of KHIKA Web GUI). Please refer [[Getting Data into KHIKA#Adding device details in the Adaptor|here]] to know [[Getting Data into KHIKA#Adding device details in the Adaptor|how to add the device to an App]]. | ||
| + | |||
| + | After making these configuration changes in KHIKA, you must apply these changes to the Workspace. Go to Configure, select the Workspace and in Workspace tab of configure menu press the Apply button as shown in the screenshot below. | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[File:Add_adapter.jpg|800px]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | Wait for a few minutes for changes to apply and data to arrive in KHIKA. With all these steps, we should now expect the data to arrive in KHIKA. Lets discover some live data in KHIKA. | ||
== How to check the output of KHIKA PaloAlto Firewall App ? == | == How to check the output of KHIKA PaloAlto Firewall App ? == | ||
| Line 14: | Line 97: | ||
=== Paloalto Suspicious Communication Dashboard=== | === Paloalto Suspicious Communication Dashboard=== | ||
| − | Go to "Dashboards" from the left menu. From the list of in-built dashboards, select this one. It shall open the Dashboard. This dashboard focuses on the | + | Go to "Dashboards" from the left menu. From the list of in-built dashboards, select this one. It shall open the Dashboard. This dashboard focuses on the communication with suspicious IP(s) and its traffic action on paloalto firewall. |
You can filter and search information and create new ones too. For help with Dashboards, click [[KHIKA Dashboards|here]] | You can filter and search information and create new ones too. For help with Dashboards, click [[KHIKA Dashboards|here]] | ||
| Line 26: | Line 109: | ||
|- | |- | ||
|Contribution of Action pie chart | |Contribution of Action pie chart | ||
| − | |Contribution of | + | |Contribution of the status of connection.Example allow, deny etc.. |
|- | |- | ||
|MaliciousIP wise Action bar graph | |MaliciousIP wise Action bar graph | ||
| − | |X axis : | + | |X axis : All the MaliciousIP(s) which communicate with device<br/> |
Y axis : MaliciousIP wise Action and it's count | Y axis : MaliciousIP wise Action and it's count | ||
|- | |- | ||
|Source wise Hits bar graph | |Source wise Hits bar graph | ||
| − | |X axis : | + | |X axis : All the Source IP(s) which initiate the connection<br/> |
Y axis : Source wise number of hits. | Y axis : Source wise number of hits. | ||
|- | |- | ||
|Destination wise Hits bar graph | |Destination wise Hits bar graph | ||
| − | |X axis : | + | |X axis : All the Destination IP(s) which communicate to malicious IP<br/> |
Y axis : DestinationIP wise number of hits. | Y axis : DestinationIP wise number of hits. | ||
|- | |- | ||
|Source wise Source Location bar graph | |Source wise Source Location bar graph | ||
| − | |X axis : | + | |X axis : All the Source IP(s) which initiate the connection(s)<br/> |
Y axis : SourceIP wise source location and it's count. | Y axis : SourceIP wise source location and it's count. | ||
|- | |- | ||
|Destination wise Destination Location bar graph | |Destination wise Destination Location bar graph | ||
| − | |X axis : | + | |X axis : All the Destination IP(s) which communicate to malicious IP<br/> |
Y axis : DestinationIP wise destination location and it's count. | Y axis : DestinationIP wise destination location and it's count. | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | | | + | |Daily Trend |
| − | |Trend of | + | |Trend of events over time. Useful to identify unusual spikes at a glance. <br/><br/>X axis : date & time <br/>Y axis : count of events |
|- | |- | ||
|Summary Table | |Summary Table | ||
| Line 58: | Line 141: | ||
==== Suggestion for useful interaction with this dashboard could be : ==== | ==== Suggestion for useful interaction with this dashboard could be : ==== | ||
| − | #Click on “MaliciousIP” in the "MaliciousIP wise Action" bar graph. This | + | #Click on “MaliciousIP” in the "MaliciousIP wise Action" bar graph. This filter is applied to rest of the dashboard and we isolate - the action of suspicious communication for selected Malicious IP. The next bar graph shall show highest hits of Source IP and Destination IP and also location of Source IP and Destination IP.The next pie chart shall show different types of action on Paloalto firewall. Details of malicious IPs can be seen in the summary table. To remove this filter, refer [[Filter information on Dashboards|here]]. |
| − | |||
=== Paloalto Config Summary Dashboard === | === Paloalto Config Summary Dashboard === | ||
| Line 78: | Line 160: | ||
|- | |- | ||
|Admin wise Command bar graph | |Admin wise Command bar graph | ||
| − | |X axis : | + | |X axis : Admin users<br/> |
Y axis : Commands fired by admin user and it's count. | Y axis : Commands fired by admin user and it's count. | ||
|- | |- | ||
|Contribution of FW IP pie chart | |Contribution of FW IP pie chart | ||
| − | |Contribution of number of firewall IP | + | |Contribution of number of firewall IP(s). |
|- | |- | ||
|FW IP wise Command bar graph | |FW IP wise Command bar graph | ||
| − | |X axis : | + | |X axis : Firewall IP(s)<br/> |
| − | Y axis : Commands fired by firewall IP | + | Y axis : Commands fired by firewall IP(s) and it's count. |
|- | |- | ||
|Contribution of Path pie chart | |Contribution of Path pie chart | ||
| − | |Contribution of path of paloalto firewall | + | |Contribution of the path of paloalto firewall |
|- | |- | ||
|Contribution of Result pie chart | |Contribution of Result pie chart | ||
| − | |Contribution of results like succeeded,submitted etc. of | + | |Contribution of results like succeeded, submitted, etc. of changed configuration. |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | | + | |Daily Trend |
| − | |Trend of | + | |Trend of events over time. Useful to identify unusual spikes at a glance.<br/><br/>X axis : date & time<br/>Y axis : count of events |
|- | |- | ||
|Summary Table | |Summary Table | ||
| Line 104: | Line 186: | ||
==== A suggestion for useful interaction with this dashboard could be : ==== | ==== A suggestion for useful interaction with this dashboard could be : ==== | ||
| − | #Click on “Command” in the "Admin wise Command" bar graph. This gets selected and shows the | + | #Click on “Command” in the "Admin wise Command" bar graph. This gets selected and shows the which commands are fired by admin user on paloalto firewall. The next bar shall show commands fired on various firewall devices. |
| − | # | + | #Click on particular "command" from "Contribution of Commands" pie chart.Then we shall show result of executed command, path and firewall device IP where a command is executed. Details of the selected command can be seen in the summary table.To remove this filter refer [[Filter information on Dashboards|here]]. |
| − | |||
=== Paloalto User Authentications Dashboard === | === Paloalto User Authentications Dashboard === | ||
| − | Go to "Dashboards" from the left menu. From the list of in-built dashboards, select this one. It shall open the Dashboard. This dashboard shows the | + | Go to "Dashboards" from the left menu. From the list of in-built dashboards, select this one. It shall open the Dashboard. This dashboard shows the detailed information about user login and logout activities and authentication failure activities occuring over the Palo Alto firewall. |
You can filter and search information and create new ones too. For help with Dashboards, click [[KHIKA Dashboards|here]] | You can filter and search information and create new ones too. For help with Dashboards, click [[KHIKA Dashboards|here]] | ||
| Line 127: | Line 208: | ||
|- | |- | ||
|User wise Status bar graph | |User wise Status bar graph | ||
| − | |X axis : | + | |X axis : Users<br/> |
Y Axis : User wise status and it's count. | Y Axis : User wise status and it's count. | ||
|- | |- | ||
| Line 133: | Line 214: | ||
|Contribution of status like authenticated,loggedin etc. on paloalto firewall. | |Contribution of status like authenticated,loggedin etc. on paloalto firewall. | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | | | + | |Daily Trend |
| − | |Trend of | + | |Trend of events over time. Useful to identify unusual spikes at a glance.<br/><br/>X axis : date & time<br/>Y axis : count of events |
|- | |- | ||
|Summary Table | |Summary Table | ||
| Line 140: | Line 221: | ||
|} | |} | ||
| − | |||
==== Some suggestions for useful interaction with this dashboard could be : ==== | ==== Some suggestions for useful interaction with this dashboard could be : ==== | ||
| − | #Click on “User” in the "User wise Status" bar graph. This gets selected and shows the | + | #Click on “User” in the "User wise Status" bar graph. This gets selected and shows the status of login/logout activity for selected User. The next pie shall show sources where users are logged in. Details of selected "user" activities can be seen in the summary table.To remove this filter refer [[Filter information on Dashboards|here]]. |
| − | |||
=== Paloalto System Summary Dashboard === | === Paloalto System Summary Dashboard === | ||
| − | Go to "Dashboards" from the left menu. From the list of in-built dashboards, select this one. It shall open the Dashboard. This dashboard shows | + | Go to "Dashboards" from the left menu. From the list of in-built dashboards, select this one. It shall open the Dashboard. This dashboard shows detailed information about the system activities on the Palo Alto Firewall. |
| − | You can filter and search information | + | You can filter and search information. For help with Dashboards, click [[KHIKA Dashboards|here]] |
==== Elements in the Dashboard are explained below : ==== | ==== Elements in the Dashboard are explained below : ==== | ||
| Line 163: | Line 242: | ||
|- | |- | ||
|Contribution of Severity pie chart | |Contribution of Severity pie chart | ||
| − | |Contribution of different types of severity like informational | + | |Contribution of different types of severity like informational. |
|- | |- | ||
|Contribution_of_Subtype pie chart | |Contribution_of_Subtype pie chart | ||
| − | |Contribution of different types of subtypes | + | |Contribution of different types of subtypes in paloalto firewall. |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | | + | |Daily Trend |
| − | |Trend of | + | |Trend of events over time. Useful to identify unusual spikes at a glance.<br/><br/>X axis : date & time<br/>Y axis : count of events |
|- | |- | ||
|Summary Table | |Summary Table | ||
| Line 175: | Line 254: | ||
|} | |} | ||
| − | |||
==== Some suggestions for useful interaction with this dashboard could be : ==== | ==== Some suggestions for useful interaction with this dashboard could be : ==== | ||
| − | # | + | #Click on particular severity in "Contribution of Severity" pie chart.This filter is applied to rest of the dashboard and it shows all the events of selected severity. Relevant details of system activity can be seen in the Summary table.To remove this filter refer [[Filter information on Dashboards|here]]. |
| − | |||
=== Paloalto Threats Detection By Application Dashboard === | === Paloalto Threats Detection By Application Dashboard === | ||
| − | Go to "Dashboards" from the left menu. From the list of in-built dashboards, select this one. It shall open the Dashboard.This dashboard shows the | + | Go to "Dashboards" from the left menu. From the list of in-built dashboards, select this one. It shall open the Dashboard.This dashboard shows the details of threats detected by Palo Alto Firewall like threat name, application name ,source country,source IP address,etc. |
You can filter and search information and create new ones too. For help with Dashboards, click [[KHIKA Dashboards|here]] | You can filter and search information and create new ones too. For help with Dashboards, click [[KHIKA Dashboards|here]] | ||
| Line 207: | Line 284: | ||
|- | |- | ||
|Source wise Threat bar graph | |Source wise Threat bar graph | ||
| − | |X axis : | + | |X axis : SourceIP(s)<br/> |
Y axis : SourceIP wise Threat and it's count. | Y axis : SourceIP wise Threat and it's count. | ||
|- | |- | ||
|Destination wise Threat bar graph | |Destination wise Threat bar graph | ||
| − | |X axis : | + | |X axis : DestinationIP(s)<br/> |
Y axis : DestinationIP Threat and it's count. | Y axis : DestinationIP Threat and it's count. | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | | | + | |Daily trend |
| − | |Trend of | + | |Trend of events over time. Useful to identify unusual spikes at a glance.<br/><br/>X axis : date & time<br/>Y axis : count of events |
|- | |- | ||
|Summary Table | |Summary Table | ||
| Line 223: | Line 300: | ||
==== Some suggestions for useful interaction with this dashboard could be : ==== | ==== Some suggestions for useful interaction with this dashboard could be : ==== | ||
| − | #Click on “ThreatName” in the "ThreatName wise Action" bar graph. This gets selected and shows the ThreatName | + | #Click on “ThreatName” in the "ThreatName wise Action" bar graph. This gets selected and shows the status of selected "ThreatName". The next bar graph shows SourceIP and DestinationIP.The next pie chart shows different types of "applications" on Paloalto firewall. Details of selected threat can be seen in the summary table.To remove this filter refer [[Filter information on Dashboards|here]]. |
| − | |||
=== Paloalto Allowed External Source Dashboard === | === Paloalto Allowed External Source Dashboard === | ||
| Line 244: | Line 320: | ||
|- | |- | ||
|Source wise Hits bar graph | |Source wise Hits bar graph | ||
| − | |X axis : | + | |X axis : SourceIP(s)<br/> |
Y axis : SourceIP wise number of hits. | Y axis : SourceIP wise number of hits. | ||
|- | |- | ||
|Destination wise Hits bar graph | |Destination wise Hits bar graph | ||
| − | |X axis : | + | |X axis : DestinationIP(s)<br/> |
Y axis : DestinationIP wise number of hits. | Y axis : DestinationIP wise number of hits. | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | | | + | |Daily trend |
| − | |Trend of | + | |Trend of events over time. Useful to identify unusual spikes at a glance.<br/><br/>X axis : date & time<br/>Y axis : count of events |
|- | |- | ||
|Summary Table | |Summary Table | ||
| Line 258: | Line 334: | ||
|} | |} | ||
| − | |||
==== A suggestion for useful interaction with this dashboard could be : ==== | ==== A suggestion for useful interaction with this dashboard could be : ==== | ||
| − | # | + | #Click on a "Source IP" in "Source wise hits" bar chart, the filter get applied to rest of the dashboard. so we can isolate - Hits for selected source IP, Destination IPs which communicate with selected Source IP, and location of Selected Source IP. Details about selected source IP can be seen in the summary table.To remove this filter refer [[Filter information on Dashboards|here]]. |
| − | |||
=== Paloalto Blocked External Source Dashboard === | === Paloalto Blocked External Source Dashboard === | ||
| Line 283: | Line 357: | ||
|- | |- | ||
|Source wise Hits bar graph | |Source wise Hits bar graph | ||
| − | |X axis : | + | |X axis : SourceIP(s)<br/> |
Y axis : SourceIP wise number of hits. | Y axis : SourceIP wise number of hits. | ||
|- | |- | ||
|Destination wise Hits bar graph | |Destination wise Hits bar graph | ||
| − | |X axis : | + | |X axis : DestinationIP(s)<br/> |
Y axis : DestinationIP wise number of hits. | Y axis : DestinationIP wise number of hits. | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | | | + | |Daily Trend |
| − | |Trend of | + | |Trend of events over time. Useful to identify unusual spikes at a glance.<br/><br/>X axis : date & time<br/>Y axis : count of events |
|- | |- | ||
|Summary Table | |Summary Table | ||
| Line 297: | Line 371: | ||
|} | |} | ||
| − | |||
==== A suggestion for useful interaction with this dashboard could be : ==== | ==== A suggestion for useful interaction with this dashboard could be : ==== | ||
| − | # | + | #Click on a "Source IP" in "Source wise hits" bar chart, this filter gets applied to rest of the dashboard. so we can isolate - Hits for selected source IP, Destination IP(s) which communicate with selected Source IP, and location of Selected Source IP. Details about selected Source IP can be seen in the summary table.To remove this filter refer [[Filter information on Dashboards|here]]. |
| − | |||
=== PaloAlto Firewall Alerts === | === PaloAlto Firewall Alerts === | ||
| Line 322: | Line 394: | ||
|- | |- | ||
|Paloalto firewall communication with suspicious ip | |Paloalto firewall communication with suspicious ip | ||
| − | |This alert is triggered when | + | |This alert is triggered when bytes are send and receive during communication with Maliacious IP. |
|Communication with a bad IP is happening, it must be blocked immediately as it could be a possible attack or data exfiltration.<br/><br/>You can check the log for this communication by simply searching the malicious IP in the logs. You can also check which internal IP addresses are communicating with this IP address and track the real users behind those internal IP addresses.<br/><br/> If you see an internal IP constantly getting involved in malicious communication (with same or multiple external IP addresses), you may install agents on the internal nodes involved and check the real user and process responsible for this communication.<br/><br/>If required, quarantine the affected internal servers till the time the issues are resolved. | |Communication with a bad IP is happening, it must be blocked immediately as it could be a possible attack or data exfiltration.<br/><br/>You can check the log for this communication by simply searching the malicious IP in the logs. You can also check which internal IP addresses are communicating with this IP address and track the real users behind those internal IP addresses.<br/><br/> If you see an internal IP constantly getting involved in malicious communication (with same or multiple external IP addresses), you may install agents on the internal nodes involved and check the real user and process responsible for this communication.<br/><br/>If required, quarantine the affected internal servers till the time the issues are resolved. | ||
|- | |- | ||
| Line 330: | Line 402: | ||
|- | |- | ||
|Paloalto firewall successful host scan activity by malicious ip | |Paloalto firewall successful host scan activity by malicious ip | ||
| − | | | + | |This alert is triggered when more than 10 connections happened from same malicious IP and status is deny followed by a successful login status using different destination port, within one minute. |
|Bad ip address tries to spray connection requests on multiple popular ports (21,22,53,80,443 etc) targetting one single IP addresses at a time with an intention to find the open ports on the target IP address. Typically, scan attempt is the first stage of reconnaissance in the attack life cycle and attacker done successful connection on open ports. <br/><br/>It is important to check the reputation of the external ip address and block the same if necessary.<br/><br/>It is also important to verify the sanity of affected internal nodes by checking if any unwarranted system policy change or software configuration/updates have occured during the affected time period. If required, quarantine the affected servers till the time the issues are resolved. | |Bad ip address tries to spray connection requests on multiple popular ports (21,22,53,80,443 etc) targetting one single IP addresses at a time with an intention to find the open ports on the target IP address. Typically, scan attempt is the first stage of reconnaissance in the attack life cycle and attacker done successful connection on open ports. <br/><br/>It is important to check the reputation of the external ip address and block the same if necessary.<br/><br/>It is also important to verify the sanity of affected internal nodes by checking if any unwarranted system policy change or software configuration/updates have occured during the affected time period. If required, quarantine the affected servers till the time the issues are resolved. | ||
|- | |- | ||
| Line 342: | Line 414: | ||
|- | |- | ||
|Paloalto firewall successful sweep scan activity by malicious ip | |Paloalto firewall successful sweep scan activity by malicious ip | ||
| − | | | + | |This alert is triggered when more than 10 connections happened from same malicious IP and status is deny followed by a successful login status using different Destination IP, within one minute. |
|Bad ip address tries to spray connection requests on one of the popular ports (21,22,53,80,443 etc) on multiple IP addresses with an intention to find which ports are opened on what IP addresses. Typically, scan attempt is the first stage of reconnaissance in the attack life cycle and attacker finds open port on one of ip addresses and is able to establish a connection.<br/><br/>It is important to check the reputation of the external ip address and block the same if necessary.<br/><br/>It is also important to verify the sanity of affected internal nodes by checking if any unwarranted system policy change or software configuration/updates have occured during the affected time period. If required, quarantine the affected servers till the time the issues are resolved. | |Bad ip address tries to spray connection requests on one of the popular ports (21,22,53,80,443 etc) on multiple IP addresses with an intention to find which ports are opened on what IP addresses. Typically, scan attempt is the first stage of reconnaissance in the attack life cycle and attacker finds open port on one of ip addresses and is able to establish a connection.<br/><br/>It is important to check the reputation of the external ip address and block the same if necessary.<br/><br/>It is also important to verify the sanity of affected internal nodes by checking if any unwarranted system policy change or software configuration/updates have occured during the affected time period. If required, quarantine the affected servers till the time the issues are resolved. | ||
|- | |- | ||
|Paloalto firewall successful sweep scan activity | |Paloalto firewall successful sweep scan activity | ||
| − | | | + | |This alert is triggered when more than 10 connections happened from the same Source IP and status is deny followed by a successful login status using different Destination IP, within one minute. |
|Attacker tries to spray connection requests on one of the popular ports (21,22,53,80,443 etc) on multiple IP addresses with an intention to find which ports are opened on what IP addresses. Typically, scan attempt is the first stage of reconnaissance in the attack life cycle and attacker done successful connection on one of ip addresses<br/><br/>It is important to check the reputation of the suspected ip address.<br/><br/>If the suspected ip address is external, you may consider blocking it.<br/><br/>If the suspected ip address is internal, you may need to verify the sanity of the corresponding device.<br/><br/>It is also important to verify the sanity of affected internal nodes by checking if any unwarranted system policy change or software configuration/updates have occured during the affected time period. If required, quarantine the affected servers till the time the issues are resolved.<br/><br/>This may be a false positve. | |Attacker tries to spray connection requests on one of the popular ports (21,22,53,80,443 etc) on multiple IP addresses with an intention to find which ports are opened on what IP addresses. Typically, scan attempt is the first stage of reconnaissance in the attack life cycle and attacker done successful connection on one of ip addresses<br/><br/>It is important to check the reputation of the suspected ip address.<br/><br/>If the suspected ip address is external, you may consider blocking it.<br/><br/>If the suspected ip address is internal, you may need to verify the sanity of the corresponding device.<br/><br/>It is also important to verify the sanity of affected internal nodes by checking if any unwarranted system policy change or software configuration/updates have occured during the affected time period. If required, quarantine the affected servers till the time the issues are resolved.<br/><br/>This may be a false positve. | ||
|- | |- | ||
|Paloalto firewall worm detected | |Paloalto firewall worm detected | ||
| − | | | + | |This alert is triggered when destination ports are('445','137','138','139') and "untrust-l3" value is available in traffic type of events. |
|Log messages indicative of a worm are detected. Check the attacking IPs in question. Verify the reputation these IPs in reputation databased such as virustotal.com, ipvoid.com etc. | |Log messages indicative of a worm are detected. Check the attacking IPs in question. Verify the reputation these IPs in reputation databased such as virustotal.com, ipvoid.com etc. | ||
|- | |- | ||
| Line 362: | Line 434: | ||
|- | |- | ||
|Paloalto firewall communication with possible IOC or bad IP | |Paloalto firewall communication with possible IOC or bad IP | ||
| − | |This alert is triggered when suspicious IP is | + | |This alert is triggered when suspicious IP is communicate with internal IP. |
|KHIKA shares community based threat intelligence (TI) every 24 hours. TI has list of IP addresses with bad reputation. Every bad IP is marked with number of communities reporting it, name of each community and confidence indicating how confident are we about the reputation. This alert is generated when communication with a bad IP is let through.<br/><br/>If communication with a bad IP is happening, it must be blocked immediately as it could be a possible attack or data exfiltration.<br/><br/>You can check how log this communication is happening by simply searching the malicious IP in the logs. You can also check what internal IP addresses are communicating with this IP addresses and track the real users behind those internal IP addresses.<br/><br/>Cross-check the reputation of the IP with popular websites such as ipvoid.com, virustotal.com.<br/><br/>If you see an internal IP constantly getting involved in malicious communication (with same or multiple external IP addresses), you may install agents on the internal nodes involved and check the real user and process responsible for this communication.<br/><br/>It is critical to block this rogue communication. | |KHIKA shares community based threat intelligence (TI) every 24 hours. TI has list of IP addresses with bad reputation. Every bad IP is marked with number of communities reporting it, name of each community and confidence indicating how confident are we about the reputation. This alert is generated when communication with a bad IP is let through.<br/><br/>If communication with a bad IP is happening, it must be blocked immediately as it could be a possible attack or data exfiltration.<br/><br/>You can check how log this communication is happening by simply searching the malicious IP in the logs. You can also check what internal IP addresses are communicating with this IP addresses and track the real users behind those internal IP addresses.<br/><br/>Cross-check the reputation of the IP with popular websites such as ipvoid.com, virustotal.com.<br/><br/>If you see an internal IP constantly getting involved in malicious communication (with same or multiple external IP addresses), you may install agents on the internal nodes involved and check the real user and process responsible for this communication.<br/><br/>It is critical to block this rogue communication. | ||
|- | |- | ||
Latest revision as of 01:51, 31 March 2020
Contents
- 1 Introduction
- 2 Enabling Syslog forwarding on the device
- 3 Verifying SYSLOG data collection
- 4 How to Install the KHIKA App for PaloAlto Firewall?
- 5 Adding the device in the Adaptor
- 6 How to check the output of KHIKA PaloAlto Firewall App ?
- 6.1 Paloalto Suspicious Communication Dashboard
- 6.2 Paloalto Config Summary Dashboard
- 6.3 Paloalto User Authentications Dashboard
- 6.4 Paloalto System Summary Dashboard
- 6.5 Paloalto Threats Detection By Application Dashboard
- 6.6 Paloalto Allowed External Source Dashboard
- 6.7 Paloalto Blocked External Source Dashboard
- 6.8 PaloAlto Firewall Alerts
Introduction
Most of the network devices, such as firewalls, switches, routers, web proxies etc send the traffic and user activity related information in the form of logs over syslog protocol. Some applications such as Oracle database server, Symantec antivirus server, EMC SAN Storage etc also support syslog protocol as syslog is very efficient and simple to integrate with. KHIKA Data Aggregator is pre-configured with syslog services on port 514. The key parts to get here are :
- Enabling Syslog forwarding on the device
- Install the KHIKA App for PaloAlto Firewall
- Get data from your PaloAlto Firewall into KHIKA Aggregator
Enabling Syslog forwarding on the device
you are recommended to refer to Paloalto documentation for enabling syslogs on your firewall device.
You can refer below suggested steps for enabling syslogs on your PaloAlto firewall device.
1.Configure a Syslog server profile
1.Select Device > Server Profiles > Syslog.
2.Click Add and enter a Name for the profile.
3.If the firewall has more than one virtual system (vsys), select the Location (vsys or Shared) where this profile is available.
4.For each syslog server, click Add and enter the information that the firewall requires to connect to it:
Name — Unique name for the server profile.
Syslog Server — IP address or fully qualified domain name (FQDN) of the syslog server.
Transport — Select TCP, UDP, or SSL as the method of communication with the syslog server.
Port —The port number on which to send syslog messages (default is UDP on port 514); you must use the same port number on the firewall and the syslog
server.
Format —Select the syslog message format to use: BSD (the default) or IETF. Traditionally, BSD format is over UDP and IETF format is over TCP or SSL.
Facility —Select a syslog standard value (default is LOG_USER) to calculate the priority (PRI) field in your syslog server implementation. Select the
value that maps to how you use the PRI field to manage your syslog messages.
5.Click OK to save the server profile.
2.Configure syslog forwarding for Traffic, Threat, and WildFire Submission logs.
1.Create a log forwarding profile.
For creating log forwarding profile please refer this log forwarding profile
Select Objects > Log Forwarding, click Add, and enter a Name to identify the profile.
For each log type and each severity level or WildFire verdict, select the Syslog server profile and click OK.
2.Assign the log forwarding profile to security rules.
For creating log forwarding profile to security rules please refer this log forwarding profile to security rules
3. Configure syslog forwarding for System, Config, HIP Match, and Correlation logs.
Select Device > Log Settings. For System and Correlation logs, click each Severity level, select the Syslog server profile, and click OK.
` For Config, HIP Match, and Correlation logs, edit the section, select the Syslog server profile, and click OK.
4. Commit your changes and review the logs on the syslog server.
Click Commit. To review the logs, refer to the documentation of your syslog management software.
Verifying SYSLOG data collection
For help to verifying syslog data collection click here.
How to Install the KHIKA App for PaloAlto Firewall?
It is assumed, that you have already configured KHIKA Data Aggregator in your environment. If not, please read how to configure KHIKA Data Aggregator and perform the pre-requisite steps.
This section explains how to pick and install the KHIKA application for PaloAlto Firewall . Installing the application shall put together and activate the adapter (parser) that can handle PaloAlto Firewall data format, the dashboards and the alert rules preconfigured.
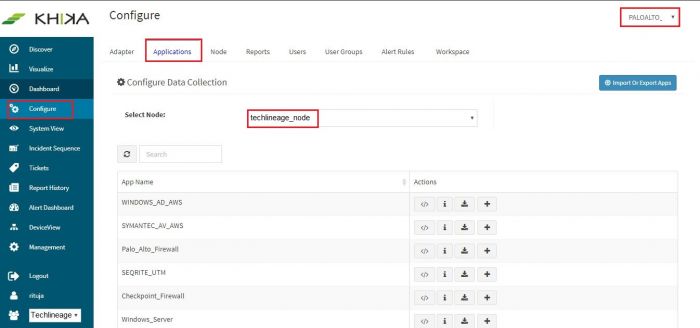
Go to “Applications” tab in the “Configure” menu.
Check whether the appropriate Workspace is selected. Note: Application is always loaded in a Workspace. Read the section on Workspaces to know more about KHIKA Workspaces. Also select your KHIKA aggregator name in the Node dropdown. This is to ensure that we are collecting data from the desired source and into the correct workspace which is ready with the configured application and components.
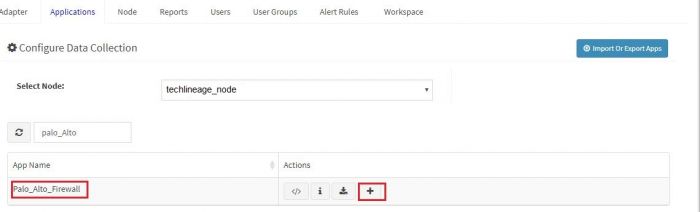
Click on the “+” button. A pop up appears.
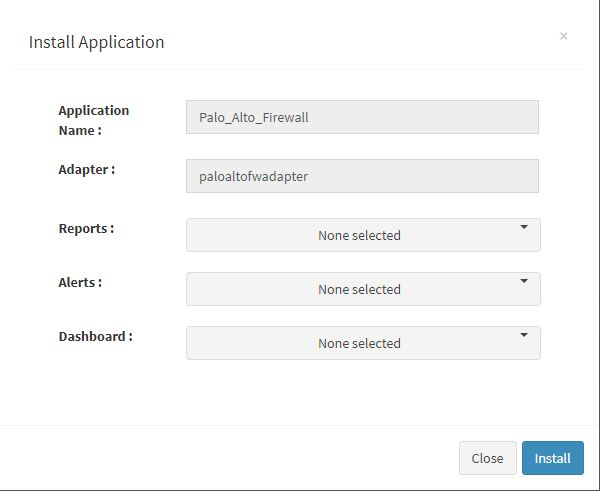
User can now select the contents of the application required. For example, on the dropdown for “Reports”, click to expand it. List of all reports can be seen. User can individually select the reports required by checking on the checkbox next to each. Alternatively, check on “Select All” option to get all of them. Similarly you can select contents from Alerts and Dashboards.
What are KHIKA Reports
What are KHIKA Dashboards
What are KHIKA Alerts
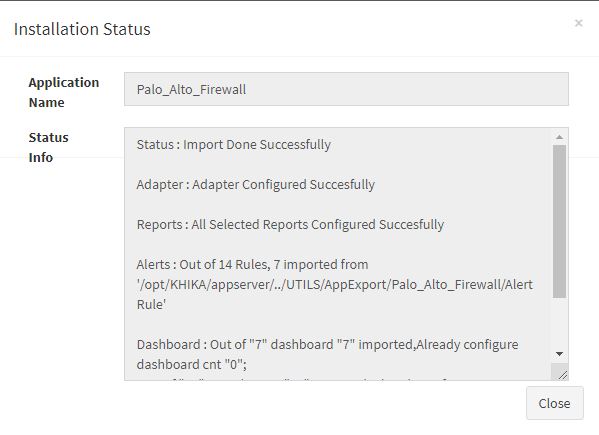
Click “OK” to proceed with the installation of the selected Application. After successful installation, following status should be displayed :
This simple procedure to install a KHIKA App, automatically configures the Adapter (required for parsing the data from raw syslogs), calculated KHIKA reports on raw data, Visualizations, Dashboards and Alerts – all in one click.
Adding the device in the Adaptor
After syslogs are enabled on the device and the App is installed into KHIKA, it is the time to add the device to the this App (in Adapter section of KHIKA Web GUI). Please refer here to know how to add the device to an App.
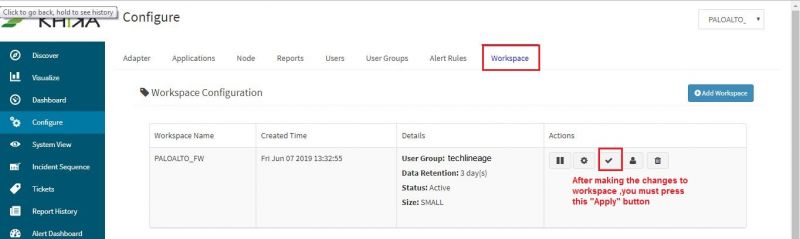
After making these configuration changes in KHIKA, you must apply these changes to the Workspace. Go to Configure, select the Workspace and in Workspace tab of configure menu press the Apply button as shown in the screenshot below.
Wait for a few minutes for changes to apply and data to arrive in KHIKA. With all these steps, we should now expect the data to arrive in KHIKA. Lets discover some live data in KHIKA.
How to check the output of KHIKA PaloAlto Firewall App ?
Paloalto Suspicious Communication Dashboard
Go to "Dashboards" from the left menu. From the list of in-built dashboards, select this one. It shall open the Dashboard. This dashboard focuses on the communication with suspicious IP(s) and its traffic action on paloalto firewall. You can filter and search information and create new ones too. For help with Dashboards, click here
Elements in the Dashboard are explained below :
| Visualization | Description |
| Contribution of Action pie chart | Contribution of the status of connection.Example allow, deny etc.. |
| MaliciousIP wise Action bar graph | X axis : All the MaliciousIP(s) which communicate with device Y axis : MaliciousIP wise Action and it's count |
| Source wise Hits bar graph | X axis : All the Source IP(s) which initiate the connection Y axis : Source wise number of hits. |
| Destination wise Hits bar graph | X axis : All the Destination IP(s) which communicate to malicious IP Y axis : DestinationIP wise number of hits. |
| Source wise Source Location bar graph | X axis : All the Source IP(s) which initiate the connection(s) Y axis : SourceIP wise source location and it's count. |
| Destination wise Destination Location bar graph | X axis : All the Destination IP(s) which communicate to malicious IP Y axis : DestinationIP wise destination location and it's count. |
| Daily Trend | Trend of events over time. Useful to identify unusual spikes at a glance. X axis : date & time Y axis : count of events |
| Summary Table | Detailed data with timestamp and count |
Suggestion for useful interaction with this dashboard could be :
- Click on “MaliciousIP” in the "MaliciousIP wise Action" bar graph. This filter is applied to rest of the dashboard and we isolate - the action of suspicious communication for selected Malicious IP. The next bar graph shall show highest hits of Source IP and Destination IP and also location of Source IP and Destination IP.The next pie chart shall show different types of action on Paloalto firewall. Details of malicious IPs can be seen in the summary table. To remove this filter, refer here.
Paloalto Config Summary Dashboard
Go to "Dashboards" from the left menu. From the list of in-built dashboards, select this one.It shall open the Dashboard.This dashboard shows the details about configuration changes made on the Palo Alto Firewall and commands executed by the user. You can filter and search information and create new ones too. For help with Dashboards, click here
Elements in the Dashboard are explained below :
| Visualization | Description |
| Contibution of Command pie chart | Names and contribution of commands which were fired on paloalto firewall. |
| Admin wise Command bar graph | X axis : Admin users Y axis : Commands fired by admin user and it's count. |
| Contribution of FW IP pie chart | Contribution of number of firewall IP(s). |
| FW IP wise Command bar graph | X axis : Firewall IP(s) Y axis : Commands fired by firewall IP(s) and it's count. |
| Contribution of Path pie chart | Contribution of the path of paloalto firewall |
| Contribution of Result pie chart | Contribution of results like succeeded, submitted, etc. of changed configuration. |
| Daily Trend | Trend of events over time. Useful to identify unusual spikes at a glance. X axis : date & time Y axis : count of events |
| Summary Table | Detailed data with timestamp and count |
A suggestion for useful interaction with this dashboard could be :
- Click on “Command” in the "Admin wise Command" bar graph. This gets selected and shows the which commands are fired by admin user on paloalto firewall. The next bar shall show commands fired on various firewall devices.
- Click on particular "command" from "Contribution of Commands" pie chart.Then we shall show result of executed command, path and firewall device IP where a command is executed. Details of the selected command can be seen in the summary table.To remove this filter refer here.
Paloalto User Authentications Dashboard
Go to "Dashboards" from the left menu. From the list of in-built dashboards, select this one. It shall open the Dashboard. This dashboard shows the detailed information about user login and logout activities and authentication failure activities occuring over the Palo Alto firewall.
You can filter and search information and create new ones too. For help with Dashboards, click here
Elements in the Dashboard are explained below :
| Visualization | Description |
| Contribution of Source pie chart | Contribution of different sources of paloalto firewall. |
| User wise Status bar graph | X axis : Users Y Axis : User wise status and it's count. |
| Contribution of Status pie chart | Contribution of status like authenticated,loggedin etc. on paloalto firewall. |
| Daily Trend | Trend of events over time. Useful to identify unusual spikes at a glance. X axis : date & time Y axis : count of events |
| Summary Table | Detailed data with timestamp and count |
Some suggestions for useful interaction with this dashboard could be :
- Click on “User” in the "User wise Status" bar graph. This gets selected and shows the status of login/logout activity for selected User. The next pie shall show sources where users are logged in. Details of selected "user" activities can be seen in the summary table.To remove this filter refer here.
Paloalto System Summary Dashboard
Go to "Dashboards" from the left menu. From the list of in-built dashboards, select this one. It shall open the Dashboard. This dashboard shows detailed information about the system activities on the Palo Alto Firewall.
You can filter and search information. For help with Dashboards, click here
Elements in the Dashboard are explained below :
| Visualization | Description |
| Contribution of Severity pie chart | Contribution of different types of severity like informational. |
| Contribution_of_Subtype pie chart | Contribution of different types of subtypes in paloalto firewall. |
| Daily Trend | Trend of events over time. Useful to identify unusual spikes at a glance. X axis : date & time Y axis : count of events |
| Summary Table | Detailed data with timestamp and count |
Some suggestions for useful interaction with this dashboard could be :
- Click on particular severity in "Contribution of Severity" pie chart.This filter is applied to rest of the dashboard and it shows all the events of selected severity. Relevant details of system activity can be seen in the Summary table.To remove this filter refer here.
Paloalto Threats Detection By Application Dashboard
Go to "Dashboards" from the left menu. From the list of in-built dashboards, select this one. It shall open the Dashboard.This dashboard shows the details of threats detected by Palo Alto Firewall like threat name, application name ,source country,source IP address,etc.
You can filter and search information and create new ones too. For help with Dashboards, click here
Elements in the Dashboard are explained below :
| Visualization | Description |
| Contribution of Action pie chart | Contribution of the actions on paloalto firewall. |
| Contribution of Application pie chart | Contribution of different types of application like web-browsing,ssl etc. on paloalto firewall. |
| ThreatName wise Action bar graph | X axis : Different types of Threat Y axis : ThreatName wise action performed and its count. |
| Source wise Threat bar graph | X axis : SourceIP(s) Y axis : SourceIP wise Threat and it's count. |
| Destination wise Threat bar graph | X axis : DestinationIP(s) Y axis : DestinationIP Threat and it's count. |
| Daily trend | Trend of events over time. Useful to identify unusual spikes at a glance. X axis : date & time Y axis : count of events |
| Summary Table | Detailed data with timestamp and count |
Some suggestions for useful interaction with this dashboard could be :
- Click on “ThreatName” in the "ThreatName wise Action" bar graph. This gets selected and shows the status of selected "ThreatName". The next bar graph shows SourceIP and DestinationIP.The next pie chart shows different types of "applications" on Paloalto firewall. Details of selected threat can be seen in the summary table.To remove this filter refer here.
Paloalto Allowed External Source Dashboard
Go to "Dashboards" from the left menu. From the list of in-built dashboards, select this one. It shall open the Dashboard. This dashboard shows the allowed external source traffic of Palo Alto firewall.
You can filter and search information and create new ones too. For help with Dashboards, click here
Elements in the Dashboard are explained below :
| Visualization | Description |
| Contribution of Source Location pie chart | Contribution of source locations of paloalto firewall. |
| Source wise Hits bar graph | X axis : SourceIP(s) Y axis : SourceIP wise number of hits. |
| Destination wise Hits bar graph | X axis : DestinationIP(s) Y axis : DestinationIP wise number of hits. |
| Daily trend | Trend of events over time. Useful to identify unusual spikes at a glance. X axis : date & time Y axis : count of events |
| Summary Table | Detailed data with timestamp and count |
A suggestion for useful interaction with this dashboard could be :
- Click on a "Source IP" in "Source wise hits" bar chart, the filter get applied to rest of the dashboard. so we can isolate - Hits for selected source IP, Destination IPs which communicate with selected Source IP, and location of Selected Source IP. Details about selected source IP can be seen in the summary table.To remove this filter refer here.
Paloalto Blocked External Source Dashboard
Go to "Dashboards" from the left menu. From the list of in-built dashboards, select this one. It shall open the Dashboard. This dashboard shows the blocked external sources traffic of Palo Alto firewall.
You can filter and search information and create new ones too. For help with Dashboards, click here
Elements in the Dashboard are explained below :
| Visualization | Description |
| Contribution of Source Location pie chart | Contribution of source locations of paloalto firewall. |
| Source wise Hits bar graph | X axis : SourceIP(s) Y axis : SourceIP wise number of hits. |
| Destination wise Hits bar graph | X axis : DestinationIP(s) Y axis : DestinationIP wise number of hits. |
| Daily Trend | Trend of events over time. Useful to identify unusual spikes at a glance. X axis : date & time Y axis : count of events |
| Summary Table | Detailed data with timestamp and count |
A suggestion for useful interaction with this dashboard could be :
- Click on a "Source IP" in "Source wise hits" bar chart, this filter gets applied to rest of the dashboard. so we can isolate - Hits for selected source IP, Destination IP(s) which communicate with selected Source IP, and location of Selected Source IP. Details about selected Source IP can be seen in the summary table.To remove this filter refer here.
PaloAlto Firewall Alerts
Alerts are generated when certain ciritical behaviour is observed in the system – real time and notified on the Alerts Dashboard in KHIKA as well as can be received in email to relevant stakeholders. The details of KHIKA Alerts are mentioned here Click on “Alert Dashboard” on left menu.
Certain alerts for paloalto firewall are pre-canned and shipped with KHIKA, keeping in mind the requirements of the users. They are mentioned in the table below :
Alerts Description
| Alert Name | Description | Suggested Resolution |
| Paloalto firewall communication with suspicious ip | This alert is triggered when bytes are send and receive during communication with Maliacious IP. | Communication with a bad IP is happening, it must be blocked immediately as it could be a possible attack or data exfiltration. You can check the log for this communication by simply searching the malicious IP in the logs. You can also check which internal IP addresses are communicating with this IP address and track the real users behind those internal IP addresses. If you see an internal IP constantly getting involved in malicious communication (with same or multiple external IP addresses), you may install agents on the internal nodes involved and check the real user and process responsible for this communication. If required, quarantine the affected internal servers till the time the issues are resolved. |
| Paloalto firewall host scan activity by malicious ip | This alert is triggered when more than 10 connections happened from same malicious IP using different destination port, within one minute | Bad ip address tries to spray connection requests on multiple popular ports (21,22,53,80,443 etc) targetting one single IP address at a time with an intention to find the open ports on the target IP address. Typically, scan attempt is the first stage of reconnaissance in the attack life cycle. It is important to check the reputation of the external ip address and block the same if necessary. |
| Paloalto firewall successful host scan activity by malicious ip | This alert is triggered when more than 10 connections happened from same malicious IP and status is deny followed by a successful login status using different destination port, within one minute. | Bad ip address tries to spray connection requests on multiple popular ports (21,22,53,80,443 etc) targetting one single IP addresses at a time with an intention to find the open ports on the target IP address. Typically, scan attempt is the first stage of reconnaissance in the attack life cycle and attacker done successful connection on open ports. It is important to check the reputation of the external ip address and block the same if necessary. It is also important to verify the sanity of affected internal nodes by checking if any unwarranted system policy change or software configuration/updates have occured during the affected time period. If required, quarantine the affected servers till the time the issues are resolved. |
| Paloalto firewall successful host scan activity | This alert is triggered when more than 10 connections happened from same Source and Destination IP and status is deny followed by successful login status using different destination port, within one minute. | Attacker tries to spray connection requests on multiple popular ports (21,22,53,80,443 etc) targetting one single IP addresses at a time with an intention to find the open ports on the target IP address. Typically, scan attempt is the first stage of reconnaissance in the attack life cycle and attacker done successful connection on open ports. It is important to check the reputation of the suspected ip address. If the suspected ip address is external, you may consider blocking it. If the suspected ip address is internal, you may need to verify the sanity of the corresponding device. It is also important to verify the sanity of affected internal nodes by checking if any unwarranted system policy change or software configuration/updates have occured during the affected time period. If required, quarantine the affected servers till the time the issues are resolved. This may be a false positve. |
| Paloalto firewall sweep scan attack by malicious ip | This alert is triggered when more than 10 connections happened from same malicious IP using different Destination IP's, within one minute. | Bad ip addresses tries to spray connection requests on one of the popular ports (21,22,53,80,443 etc) on multiple IP addresses with an intention to find which ports are opened on what IP addresses. Typically, scan attempt is the first stage of reconnaissance in the attack life cycle. It is important to check the reputation of the external ip address and block the same if necessary. |
| Paloalto firewall successful sweep scan activity by malicious ip | This alert is triggered when more than 10 connections happened from same malicious IP and status is deny followed by a successful login status using different Destination IP, within one minute. | Bad ip address tries to spray connection requests on one of the popular ports (21,22,53,80,443 etc) on multiple IP addresses with an intention to find which ports are opened on what IP addresses. Typically, scan attempt is the first stage of reconnaissance in the attack life cycle and attacker finds open port on one of ip addresses and is able to establish a connection. It is important to check the reputation of the external ip address and block the same if necessary. It is also important to verify the sanity of affected internal nodes by checking if any unwarranted system policy change or software configuration/updates have occured during the affected time period. If required, quarantine the affected servers till the time the issues are resolved. |
| Paloalto firewall successful sweep scan activity | This alert is triggered when more than 10 connections happened from the same Source IP and status is deny followed by a successful login status using different Destination IP, within one minute. | Attacker tries to spray connection requests on one of the popular ports (21,22,53,80,443 etc) on multiple IP addresses with an intention to find which ports are opened on what IP addresses. Typically, scan attempt is the first stage of reconnaissance in the attack life cycle and attacker done successful connection on one of ip addresses It is important to check the reputation of the suspected ip address. If the suspected ip address is external, you may consider blocking it. If the suspected ip address is internal, you may need to verify the sanity of the corresponding device. It is also important to verify the sanity of affected internal nodes by checking if any unwarranted system policy change or software configuration/updates have occured during the affected time period. If required, quarantine the affected servers till the time the issues are resolved. This may be a false positve. |
| Paloalto firewall worm detected | This alert is triggered when destination ports are('445','137','138','139') and "untrust-l3" value is available in traffic type of events. | Log messages indicative of a worm are detected. Check the attacking IPs in question. Verify the reputation these IPs in reputation databased such as virustotal.com, ipvoid.com etc. |
| Paloalto firewall backdoor activity detected | This alert is triggered when connection happened using vulnerable Destination ports like 3127,3198,6129,7080,within one minute. | This event indicates that a traffic is generated from internal machine on vulnerable ports(3127,3198,6129,7080). Typically, these ports are used by attacker to exploit vulnerable programs listening on these ports. Check is these ports are open and on what servers. Do you really need these ports opened? Check what programs are running on these ports. Check vulnerability reports of the applications\nBlock these ports for external traffic, unless mandatory to keep them opened. If you have to keep any of these ports opened, try to restrict the access to legitimte IPs. If you get a suspicious IP repetatively trying to access these port, block the IP. Check the reputation of the IP on popular website such as ipvoid.com, virustotal.com etc. |
| Paloalto firewall host scan attack | This alert is triggered when more than 10 connections happened from same Source and Destination IP using different destination port, within one minute. | An attacker tries to spray connection requests on multiple popular ports (21,22,53,80,443 etc) targetting one single IP addresses at a time with an intention to find the open ports on the target IP address. Typically, scan attempt is the first stage of reconnaissance in the attack life cycle. Unless it is a known and legitimate IP address performing the scan, it is important to block this IP. You may whitelist the known IP addresses (such as designated Vulnerability Scanner, Asset Discovery Tools etc), so as to supress the false positives. |
| Paloalto firewall communication with possible IOC or bad IP | This alert is triggered when suspicious IP is communicate with internal IP. | KHIKA shares community based threat intelligence (TI) every 24 hours. TI has list of IP addresses with bad reputation. Every bad IP is marked with number of communities reporting it, name of each community and confidence indicating how confident are we about the reputation. This alert is generated when communication with a bad IP is let through. If communication with a bad IP is happening, it must be blocked immediately as it could be a possible attack or data exfiltration. You can check how log this communication is happening by simply searching the malicious IP in the logs. You can also check what internal IP addresses are communicating with this IP addresses and track the real users behind those internal IP addresses. Cross-check the reputation of the IP with popular websites such as ipvoid.com, virustotal.com. If you see an internal IP constantly getting involved in malicious communication (with same or multiple external IP addresses), you may install agents on the internal nodes involved and check the real user and process responsible for this communication. It is critical to block this rogue communication. |
| Paloalto firewall sweep scan attack | This alert is triggered when more than 10 connections happened from same source IP to various Destination IP's,within one minute. | An attacker tries to spray connection requests on one of the popular ports (21,22,53,80,443 etc) on multiple IP addresses with an intention to find which ports are opened on what IP addresses. Typically, scan attempt is the first stage of reconnaissance in the attack life cycle. Unless it is a known and legitimate IP address performing scan, it is important to block this IP. You may whitelist the known IP addresses (such as designated Vulnerability Scanner, Asset Discovery Tools etc), so as to supress the false positives. |
| Paloalto firewall suspicious ip related activity from internal | This alert is triggered when suspicious IP is communication with internal IP | KHIKA shares community based threat intelligence (TI) every 24 hours. TI has list of IP addresses with bad reputation. Every bad IP is marked with number of communities reporting it, name of each community and confidence indicating how confident are we about the reputation. This alert is generated when communication with a bad IP from internal source. If communication with a bad IP is happening, it must be blocked immediately as it could be a possible attack or data exfiltration. You can check how log this communication is happening by simply searching the malicious IP in the logs. You can also check what internal IP addresses are communicating with this IP addresses and track the real users behind those internal IP addresses. Cross-check the reputation of the IP with popular websites such as ipvoid.com, virustotal.com If you see an internal IP constantly getting involved in malicious communication (with same or multiple external IP addresses), you may install agents on the internal nodes involved and check the real user and process responsible for this communication. It is critical to block this rogue communication. |
| Paloalto firewall high ICMP request from single host | This alert is triggered when 10 events of ICMP protocol is used by same source occured within 1 min | ICMP probe is an old and established technique used by attackers as the first step that involves reconnaissance. This is used to check what IPs/Hosts are responding to the ping request so that further targeted can be launched on the responding IPs/Hots. The probing IP, if not a legitimate IP, ,it should be blocked at the periphery. Check the reputation of the probing IP in external reputation databases, such as VirtusTotal.com or IPVoid.com etc. If the reputation is found to be dubious or bad, you must block such IPs. |